Interface and API
15. Use Prefix Names to Avoid Namespace Clashes
为类名添加前缀,与你的公司或应用名相关。
16: Have a Designated Initializer
提供一个 designated initializer,其它的初始化方法均应调用此方法。
17: Implement the description Method
This compact description can be used by forming a dictionary within your own description method and returning a string containing this dictionary’s description method.
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p, %@>",
[self class],
self,
@{@"title":_title,
@"latitude":@(_latitude),
@"longitude":@(_longitude)}];
}
Another method to be aware of is debugDescription, called when you invoke the print-object command within the debugger. The default implementation within the NSObject class simply calls directly through to description.
18. Prefer Immutable Objects
笔者建议大家尽量减少对象中的可变内容。在编程实践中,应该尽量把对外公布的属性设为只读,而且只在确有必要时才对外公布属性。有一些数据可能源自网络服务,它不会被修改,即使临时修改了也不会被推送到服务器。
不要把可变的 collection 作为属性公开!而应提供相关的方法。
19: Use Clear and Consistent Naming
Follow the naming that has become standard in Objective-C to create interfaces that fit in and feel right.
Ensure that method names are concise but precise, and make their use read left to right just like a sentence.
20: Prefix Private Method Names
When writing a class implementation, it is common to write methods that are used only internally. For such methods, I suggest that you prefix their names with something. This helps with debugging by clearly separating the public methods from the private ones.
21. Objective-C Error Model
Use exceptions only for fatal errors that should bring down the entire application.
For nonfatal errors, either provide a delegate method to handle errors or offer an out-parameter NSError object.
22. NSCopying
Implement the NSCopying protocol if your object will need to be copied.
浅复制(浅拷贝、指针拷贝、shallow copy):没有产生新对象,仍然指向同一块内存空间。
- 源对象和副本对象是同一对象;
- 源对象引用计数 +1,相当于做一次 retain 操作。
深复制(深拷贝、内容拷贝、deep copy):产生了新对象,存放在一块新的内存空间,与原来的对象互不影响。
- 源对象和副本对象是不同的两个对象;
- 源对象引用计数不变,副本对象计数为 1(因为是新产生的)。
- 集合的深复制只复制容器本身,集合内的元素还是原来的元素(指向同一块内存)。
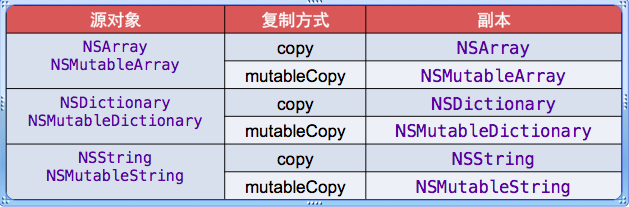
只有源对象和副本对象都不可变时,才是浅复制,其他都是深复制。
Demo *demo1 = [[Demo alloc]init];
Demo *demo2 = [[Demo alloc]init];
NSArray *arr = @[demo1, demo2];
NSMutableArray *mutableArr = [arr mutableCopy];
NSLog(@"%p, %p", arr, mutableArr); // 集合深拷贝
NSLog(@"%p, %p", [arr objectAtIndex:0], [mutableArr objectAtIndex:0]); // 集合中的对象还是指向同一块内存